Now Reading: Blood MYTH is red NOT blue
-
01
Blood MYTH is red NOT blue
Blood MYTH is red NOT blue
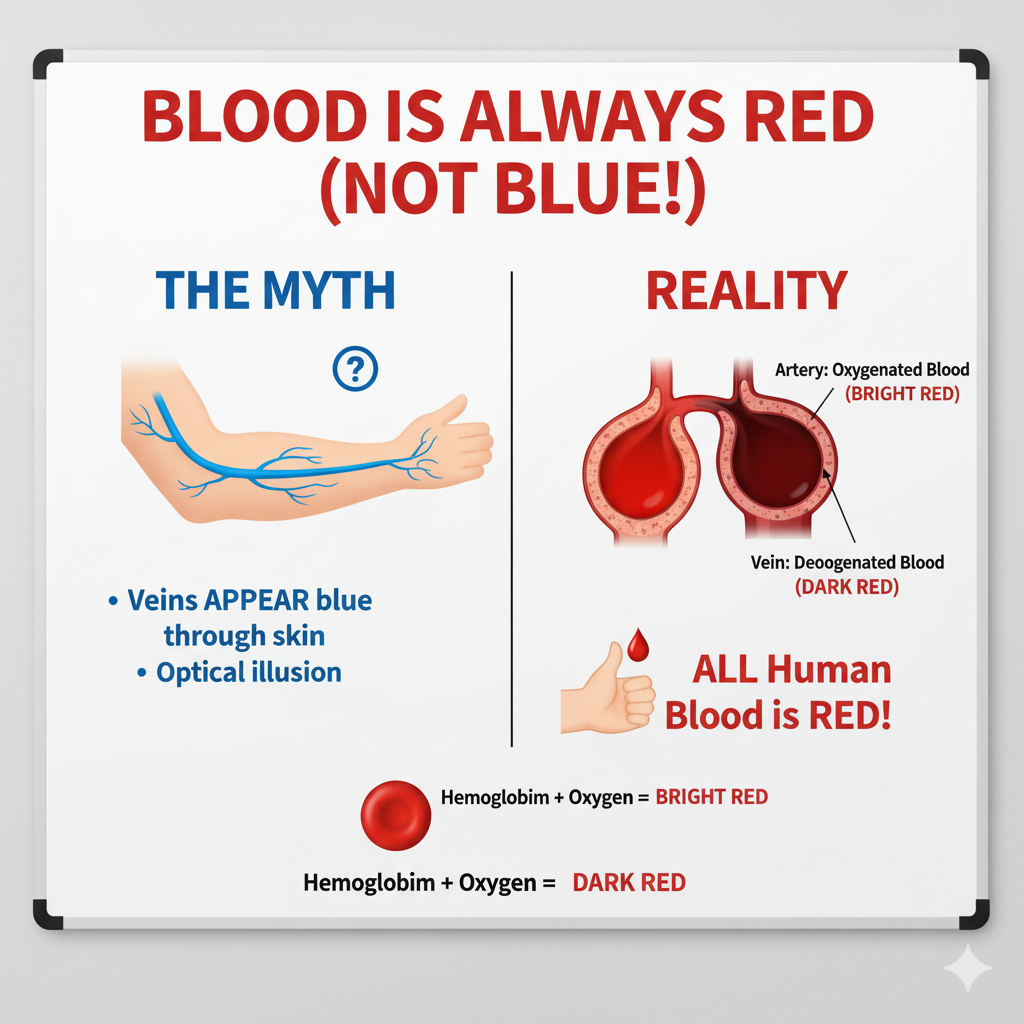
That’s a myth. Human blood is always red, and it does not turn red when it hits the air.
The misconception that blood is blue inside the body and only turns red upon exposure to air likely stems from two things:
The appearance of veins: Veins carrying deoxygenated blood often appear blue or greenish through the skin. This is an optical illusion caused by how light interacts with the skin and underlying blood vessels, not the actual color of the blood.
Deoxygenated vs. Oxygenated Blood: Blood does change color based on its oxygen content, but the colors are shades of red:
- Oxygenated blood (like that in your arteries) is bright, light cherry red.Deoxygenated blood (like that returning to your heart in your veins) is a darker, almost reddish-black or deep red.
ed. The difference in color is due to the protein hemoglobin in red blood cells. When hemoglobin binds to oxygen, it changes structure, making the blood a brighter red. When it releases oxygen, it reverts to a darker shade of red. If you have your blood drawn from a vein, you can see that the deoxygenated blood is dark red before it ever touches the air.
Extra about blood….
⚖️ Volume and Production
- How much blood? An average adult has about 5 liters (10.5 pints) of blood, which is approximately 7-8% of their total body weight.
- Where is it made? All blood cells are produced in the bone marrow—the spongy tissue inside your bones.
- Lifespan: A red blood cell has a relatively short life, lasting about 120 days before being recycled, which is why your body is constantly producing new ones.
🅰️ Blood Types and Universal Donors
- Blood Types: Human blood is categorized into eight main types (A, B, AB, and O, each with a positive or negative Rh factor). These types are determined by specific molecules (antigens) on the surface of your red blood cells.
- Transfusions: Receiving the wrong blood type can trigger a fatal immune reaction as the body attacks the foreign cells.
- Universal Donor: O negative blood is considered the “universal donor” because it lacks both A and B antigens and the Rh factor, meaning it can be safely given to almost anyone in an emergency.
- Universal Recipient: AB positive blood is the “universal recipient” because people with this type have all the common antigens, so they can generally receive blood from any other group.
🌍 Fun Facts
- Not all blood is red: While humans and all other mammals have red blood (due to the iron in hemoglobin), other creatures use different oxygen-carrying proteins:
- Some invertebrates like spiders, octopuses, and crabs have blue blood (due to the copper-containing protein hemocyanin).
- Certain marine worms have green or even violet blood.
- Trace elements: Human blood contains trace amounts of various metals, including iron (which is central to hemoglobin) and even very tiny amounts of gold.
- Bloodletting: Throughout much of history, a medical practice called “bloodletting” was performed, based on the incorrect belief that draining “excess” blood could cure illness. Thankfully, modern medicine uses blood to save lives!